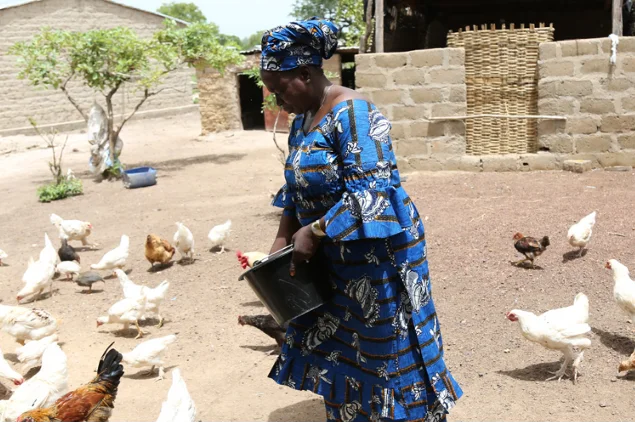
Sustainable agriculture provides a lifeline to Mali’s women

Agriculture is often a key route out of poverty for many in developing countries, especially among women.
In Mali, it is estimated that women make up half of all those involved in agriculture. However, UN Women reports that climate change is threatening to undo the progress made in building stronger rural communities and ending hunger in the country.
The UN entity, formed seven years ago, has been implementing a new programme called AgriFed, designed to combat the negative impacts of climate change on women.
“The effects of climate change are not sparing Mali, and are hitting this country hard, an additional challenge in an extremely fragile security context in the Sahel region,” says Maxime Houinato, UN Women Country Representative in Mali. “And yet, Mali, although a low contributor to the global emission of greenhouse gases, is no less committed to the race to adapt to the effects of climate change.”
AgriFed started its activities in the region of Segou, approximately 200 kilometers from Mali’s capital, Bamako. Its initial plan was to train 247 women and 66 men in sustainable agriculture techniques. This includes water conservation, new techniques in cultivation, and scheduling crops.
Women have also learned the benefits of using fertilizer and pesticides to ward off parasites. The region has seen an increased number of these creatures, which can ruin entire crops, as a direct result of rising temperatures and humidity.
“We thought the land was sick,” said local farmer Fatou Dembele. “We didn’t know that there were live parasites that attacked the roots of the plants and could kill them.”
In addition, UN Women has helped increase the local incomes of 110 women by introducing modern preservation techniques for produce such as shallots, onions, and potatoes.
Another local farmer, Alphonsine Dembele, highlighted how AgriFed has not only boosted her income but also “helped improve nutrition at home and reduce malnourishment in our children.”
The programme has also brought women from different ethnic communities together to discuss new techniques and improve harvest yields.
UN Women hopes that the success of the scheme can be replicated in other African countries, which also face similar impacts from climate change.
 Albania
Albania Algeria
Algeria Andorra
Andorra Argentina
Argentina Armenia
Armenia Australia
Australia Austria
Austria Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Bahrain
Bahrain Belgium
Belgium Bolivia
Bolivia Brazil
Brazil Bulgaria
Bulgaria Cambodia
Cambodia Cameroon
Cameroon Canada
Canada Chad
Chad Chile
Chile China
China Colombia
Colombia Costa Rica
Costa Rica Croatia
Croatia Cyprus
Cyprus Czechia
Czechia Denmark
Denmark Ecuador
Ecuador Egypt
Egypt Finland
Finland France
France Georgia
Georgia Germany
Germany Ghana
Ghana Greece
Greece Hungary
Hungary Iceland
Iceland India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Ireland
Ireland Italy
Italy Jamaica
Jamaica Japan
Japan Jordan
Jordan Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kenya
Kenya Kuwait
Kuwait Latvia
Latvia Lebanon
Lebanon Libya
Libya Lithuania
Lithuania Luxembourg
Luxembourg Malaysia
Malaysia Maldives
Maldives Mali
Mali Malta
Malta Mexico
Mexico Moldova
Moldova Monaco
Monaco Morocco
Morocco Netherlands
Netherlands New Zealand
New Zealand Nigeria
Nigeria North Macedonia
North Macedonia Norway
Norway Oman
Oman