Sustainable Charcoal Production Using Energy Efficient Kilns

Sustainable Charcoal Production in Kenya
Charcoal production is a significant industry in Kenya, serving as the main energy source for many households. Over 82 percent of urban and 34 percent of rural households rely on charcoal, employing over 700,000 people along the value chain. Despite its importance, the sector remains largely informal and unregulated, contributing significantly to deforestation due to unsustainable wood production practices.
Challenges in the Charcoal Sector
- Informality and Lack of Regulation: The charcoal sector lacks clear policies and regulations, leading to unsustainable practices and environmental degradation.
- Deforestation: Unsustainable production methods are a major contributor to deforestation, as producers do not prioritize sustainable wood sourcing.
UNDP and Local Partnerships for Sustainable Solutions
To address these challenges, the UNDP, in collaboration with the Kenya Forest Service (KFS) and Kenya Forest Research Institute (KEFRI), is implementing training programs in Taita Taveta and Kwale Counties. These programs focus on introducing sustainable technologies and practices to charcoal producers.
Key Training Components
- Sustainable Tree Utilization: Training on natural regeneration techniques to ensure a continuous supply of wood without depleting forest resources.
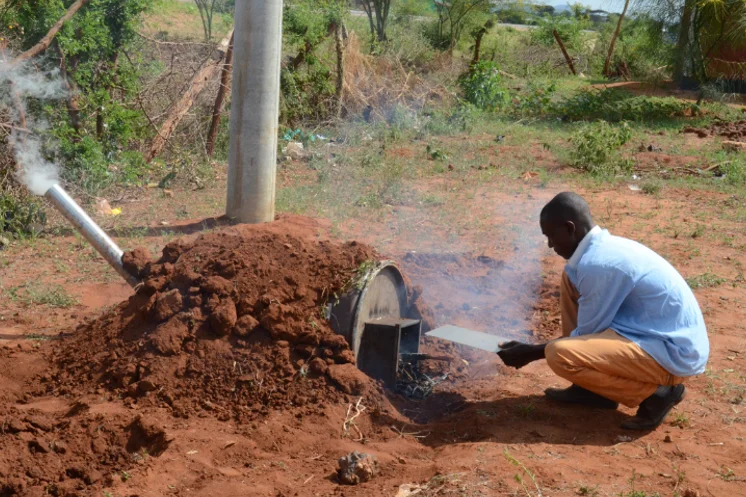
- Efficient Wood Conversion Technologies: Introduction of metal kilns, such as vertical and horizontal drum kilns, which are more efficient than traditional earth kilns.
- Regulatory Awareness: Educating producers on the charcoal act and laws governing the sector to ensure compliance and sustainable practices.
- Value Addition and Marketing: Training on branding and marketing charcoal to add value and increase producer benefits.
- Reforestation and Conservation Plans: Encouraging reforestation efforts to offset the environmental impact of charcoal production.
Innovative Technologies
- Vertical Drum Kiln: Made from ordinary oil drums, these kilns are modified with a chimney and can carbonize wood in about 8 hours, significantly faster than earth kilns which take 2 to 3 days. The recovery rate of charcoal is also higher.
- Horizontal Drum Kiln: Similar to the vertical drum kiln, this version places wood horizontally and is slightly covered with earth. It features a removable lid and a metal grill for air circulation during carbonization.
- Portable Metal Kiln: Larger kilns that can produce up to 5 bags of charcoal within 6 to 8 hours. They operate on a reverse draught principle, carbonizing wood from the top down and producing tar as a byproduct, which can be used for various purposes such as shoe polish.
Impact and Producer Feedback
Producers have shown enthusiasm for the new technologies. Martha Wambona, a local charcoal producer, expressed her intention to adopt the vertical drum kiln due to its efficiency and the high quality of the charcoal produced. The training and introduction of these technologies aim to make charcoal production more sustainable and beneficial for the producers.
By streamlining the industry and promoting sustainable practices, these initiatives aim to reduce deforestation, improve the livelihoods of charcoal producers, and ensure the long-term viability of the charcoal sector in Kenya.
 Albania
Albania Algeria
Algeria Andorra
Andorra Argentina
Argentina Armenia
Armenia Australia
Australia Austria
Austria Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Bahrain
Bahrain Belgium
Belgium Bolivia
Bolivia Brazil
Brazil Bulgaria
Bulgaria Cambodia
Cambodia Cameroon
Cameroon Canada
Canada Chad
Chad Chile
Chile China
China Colombia
Colombia Costa Rica
Costa Rica Croatia
Croatia Cyprus
Cyprus Czechia
Czechia Denmark
Denmark Ecuador
Ecuador Egypt
Egypt Finland
Finland France
France Georgia
Georgia Germany
Germany Ghana
Ghana Greece
Greece Hungary
Hungary Iceland
Iceland India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Ireland
Ireland Italy
Italy Jamaica
Jamaica Japan
Japan Jordan
Jordan Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kenya
Kenya Kuwait
Kuwait Latvia
Latvia Lebanon
Lebanon Libya
Libya Lithuania
Lithuania Luxembourg
Luxembourg Malaysia
Malaysia Maldives
Maldives Mali
Mali Malta
Malta Mexico
Mexico Moldova
Moldova Monaco
Monaco Morocco
Morocco Netherlands
Netherlands New Zealand
New Zealand Nigeria
Nigeria North Macedonia
North Macedonia Norway
Norway Oman
Oman